If you are a practitioner in the international trade industry, especially in the field of quality work, then you must be familiar with the term AQL, AQL Sampling, AQL Chart, and AQL Table. Any form of trade needs to guarantee the quality of the products. It’s normal for you to give money and get value for money. So, is there any way we can guarantee that the whole batch of products is 100% perfect? Obviously not. Is there a way to control the quality level to the limit that you can accept? Sure, that’s AQL.
AQL- As Its Name Implies
AQL means Acceptance Quality Limit, and some interpret it as Acceptance Quality Level. In the latest ISO interpretation, the word “level” has been officially replaced by “limit“. It sets the maximum number of defective individuals that can be allowed in the same batch of products to be shipped. Once the number of defective individuals exceeds this number, the whole batch of goods will be rejected.
Why AQL?
Lack of inspection is potentially disastrous
If the purchased product is not inspected, there will be no confidence in the quality of the entire batch. In any sense, it is a huge risk to spend a lot of money to purchase a batch of products with no confidence in their quality; It is a disaster for your company to receive a batch of low quality or even completely unusable products after long-distance international shipment.
No way to inspect each unit of whole batch of products
In bulk trade, it is not practical to inspect 100% of the whole batch of products to ensure the quality. First, the cost of doing so will be very high. Second, some products, such as food and disposable consumables, are not applicable to 100% inspection at all. For some products with complex structure and function, the inspection time will be very long, and some inspection will have to destroy the structure and function of the product itself to carry out, it will cause the scrap of the product.
ISO standard based sampling plan: AQL sampling
As a result, there are AQL sampling standard developed according to ISO standards and used internationally. With reasonable quality inspection, you can confidently purchase from any country or region in the world and receive the quality products you expected. Sampling and inspection based on AQL makes it reasonable to accept and reject a batch of goods, and both buyers and sellers can accept it.
Common misunderstanding of AQL
Some newcomers will simply interpret the number following AQL as a percentage – for example, when we talk about AQL2.5, he/she might suppose that the acceptable level of quality is at 2.5% of the sample taken. In fact, this understanding is incomplete. The AQL chart is a complex but logical chart, and whether 2.5 or 4.0, it is a base near the percentage upper limit, rather than a simple and precise benchmark.
AQL table, or AQL chart, or ANSI table
AQL table, or AQL chart, also called ANSI table is a set of tables or charts that are reference tool for quality inspection based on AQL standards. It was designed to make it easy for users to determine the number of samples required for quality inspection and the number of defect units allowed based on a given AQL. These tables are part of ISO2859 and are equivalent in all national and international standardization organizations, including ANSI. Most buyers and sellers in the world are familiar with this, or should be.
Whether it’s any type of quality inspection, the retailer’s own inspection, the importer’s inspection, or outsourcing the work to an independent third-party quality inspection company such as inXpection, using these forms makes it easy to determine the exact parameters necessary to properly check and verify the quality of an order before accepting and shipping it.
The whole AQL table and chart is divided into two parts, one is Sample Size Code Letters
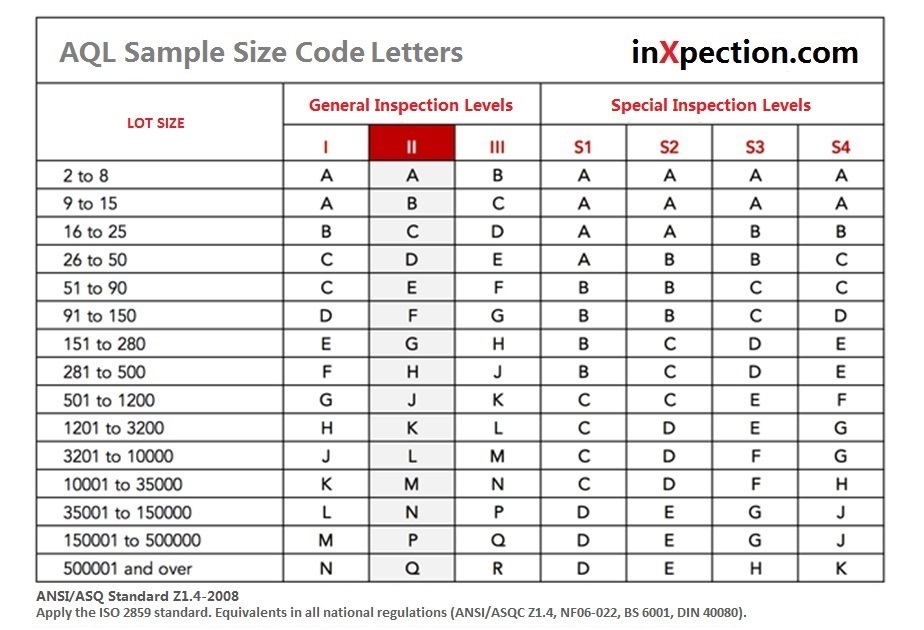
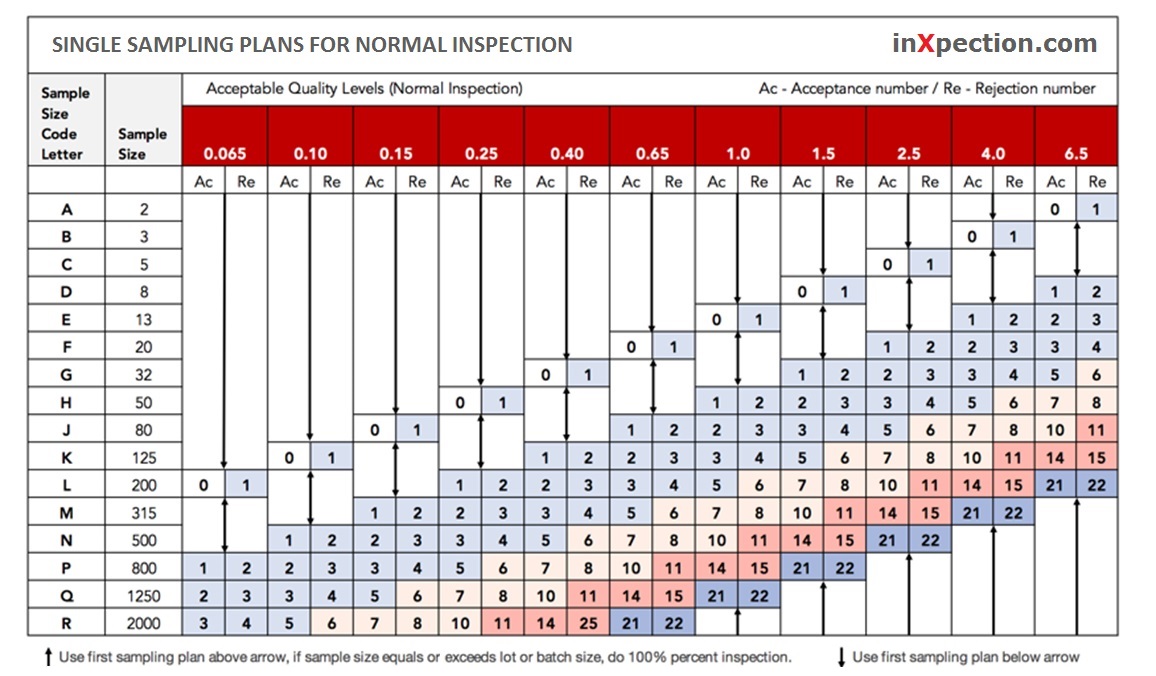
and the other is Single Sampling Plans for Normal Inspection.
Three levels of defects
You have noticed that we use Critical, Major and Minor to classify the defects found in quality inspection.
Critical defects usually refer to the most serious type in defect classification. This kind of problem may be a violation of a country’s laws and regulations, or may cause harm to human body, or may be harmful to biological invasion, and so on. Generally speaking, importers and retailers in any country have zero tolerance for such defects.
Major defects refer to appearance defects, product function defects, size errors, etc., which will affect product sales. Such problems have a small acceptance, but manufacturers should try to avoid them in production.
Minor defects refer to the problems that will not affect the use of the product, and some consumers may not pay special attention to it, but in terms of quality, it can not meet the quality requirements of the product, for example, threads that are more than 1/2 inch long, scratches that can still be seen beyond the length of one arm, and so on.
How Do You Determine A Sampling Plan?
For the person in charge of a quality department, or the person responsible for a particular project, the sampling plan might be a difficult part. Generally, the appropriate AQL for consumer goods are as below:
-
- Critical Defects: 0,
- Major Defects: AQL2.5
- MInor Defects: AQL4.0
A detailed AQL standard depends not only on the category of the product, but also on the level of quality control of the supplier producing the product, and the overall level of quality control of the raw material supply chain. In international trade, you can negotiate acceptance quality limit with the factory work with and continuously improve the quality system as the factory’s production level improves.
Step by step tutorials
Let’s take a step-by-step look at how to understand and use AQL Table or Chart. or ANSI table. We will avoid trying to explain obscure ISO-related quality systems or related terminology, instead, we express them in a way that is easy to understand.
Let’s start with an example:
Abroad Importers Inc ordered 30,000 knitted baskets from a Chinese household goods manufacturer. All products will be shipped in one batch. Buyer and the manufacturer agree to use below AQL standards in the commercial agreement:
-
- Critical defects: AQL 0.0
- Major defects: AQL 2.5
- Minor defects: AQL 4.0
How do you determine sample size for inspection, and quntity of defects that may trigger a rejection?
Step 1: Find the relevant quantity number in the rows
The order quantity is 30,000, so find the range where 30,000 is.
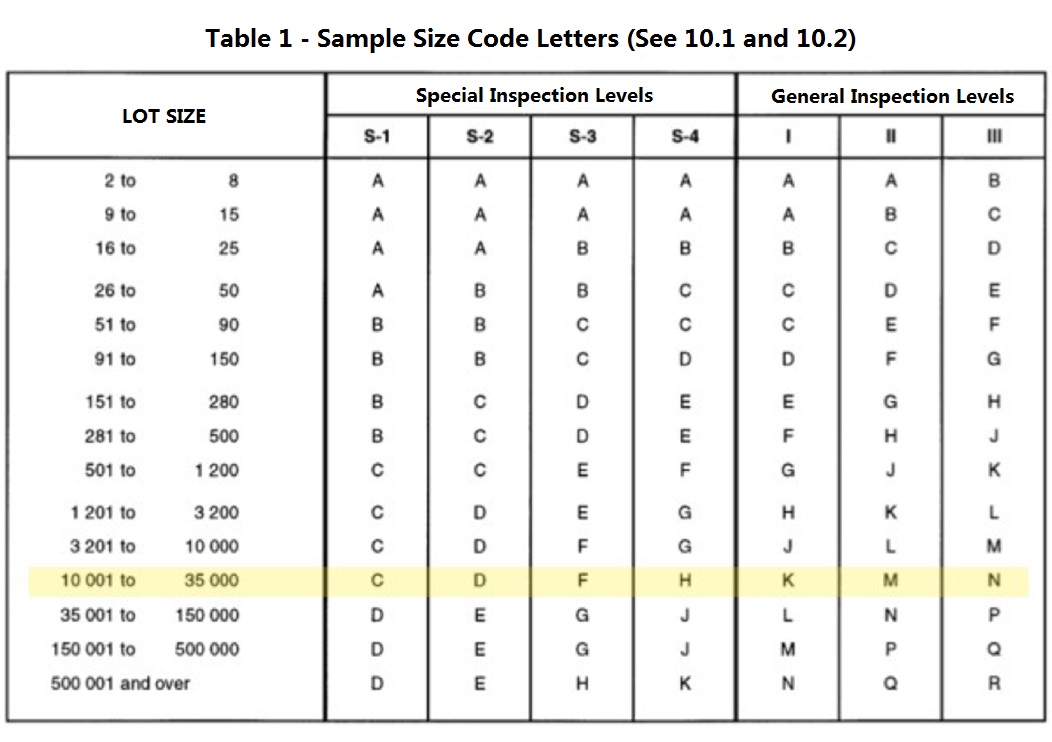
Step 2: Identify the appropriate scenario and find the appropriate columns
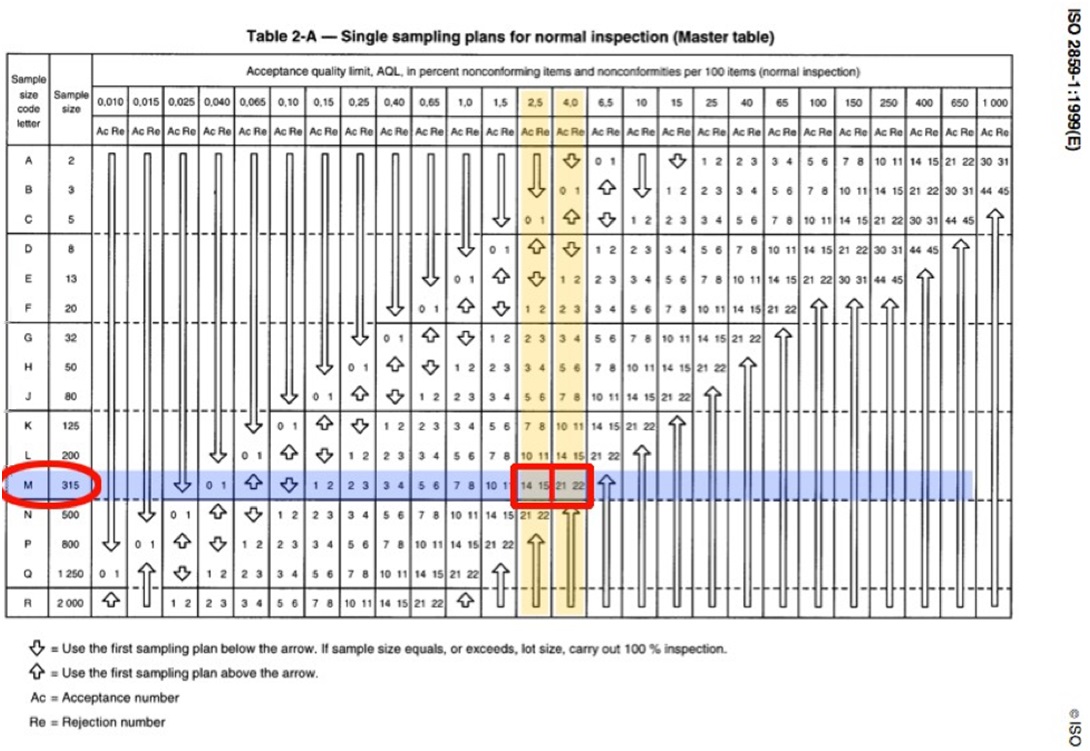
General Inspection Level II is the common used inspection level for everyday household consumer good. In our example, you can see that the rows and columns intersect at the letter M. At this time, it can be confirmed that M will be used in table 2-A below to further confirm other information of this inspection.
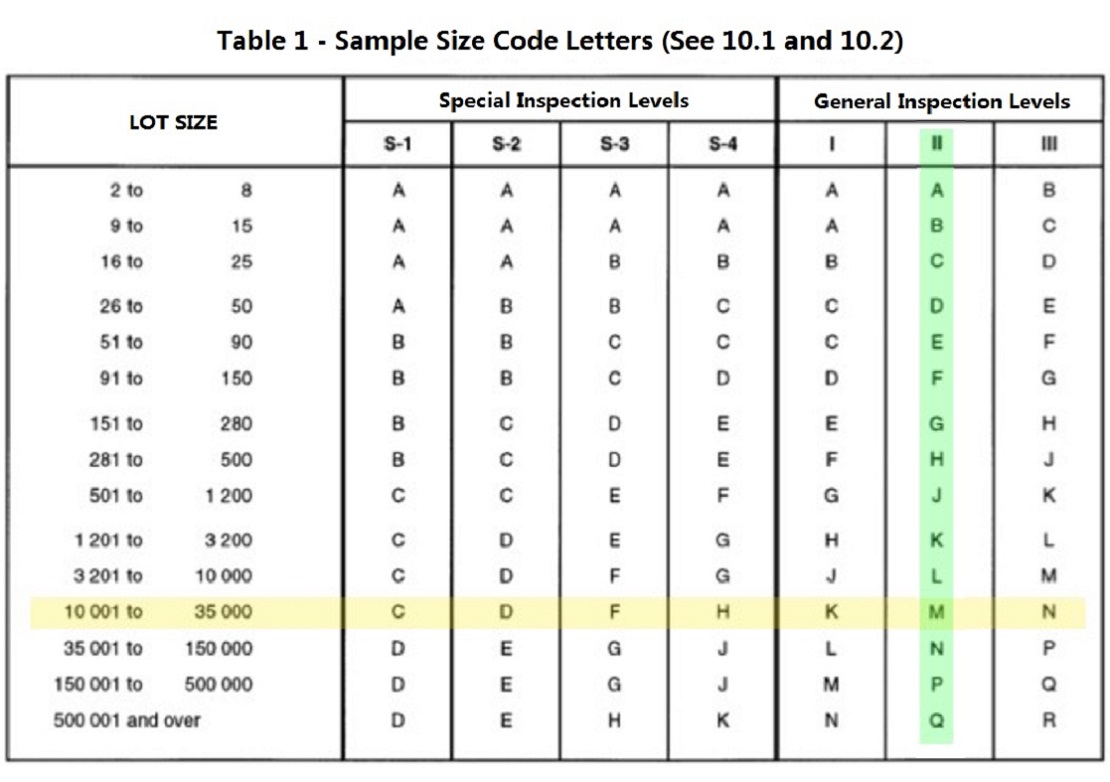
Step 3: Find the letter M and its column in Table 2-A, and determine the sample size corresponding to the sample size code letter according to the intersection of two lines
After finding the letter M, we can see that the corresponding sample number in table 2-A is 315. This means that the sample size this time is 315.
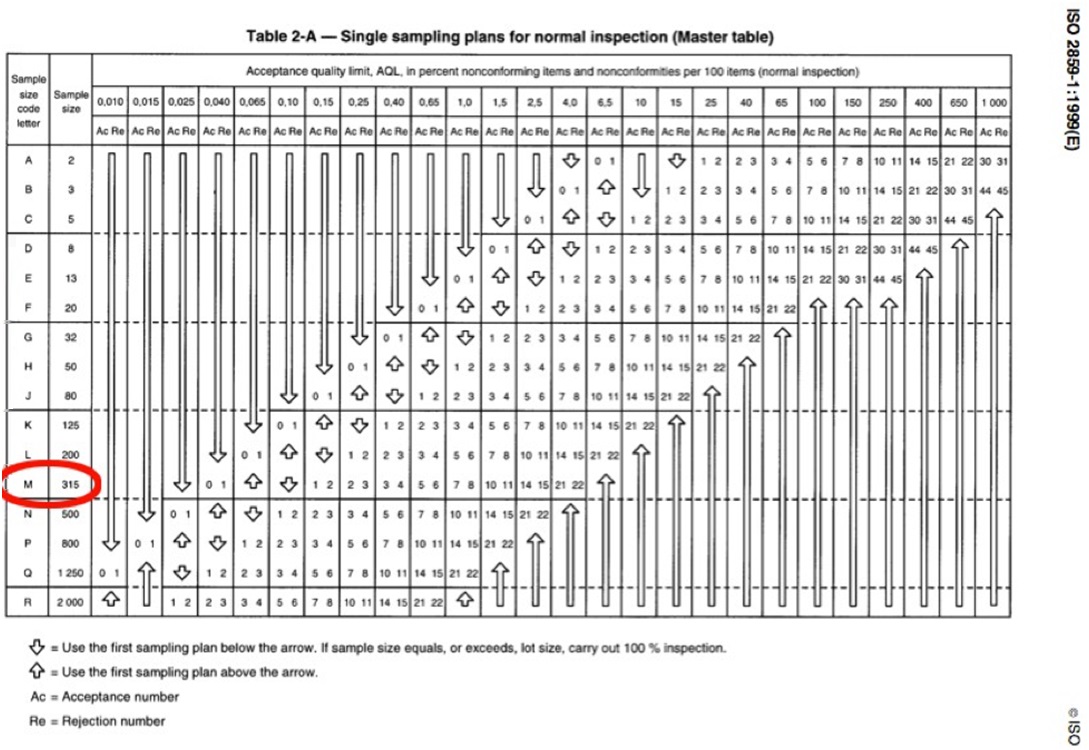
Step 4: Determine the number of defects allowed by AQL, and then the quality inspection results.
Critical Defects: AQL 0, which means that any single sample with key defects will lead to the unqualified whole batch.
Major Defects: AQL2.5. Numbers 14 and 15 are displayed at the intersection of 2.5% columns after M rows. That means if 15 or more major defects are found, the whole batch will be rejected.
MInor Defects: AQL4.0. The intersections of M rows and 4.0% columns show 21 and 22, which means that 21 or less minor defects will result in receiving the whole batch, while 22 or more minor defects will result in rejection.
AQL sampling is scientific
AQL standards allow you to develop different acceptance criteria for different levels of defects, so that you do not reject a whole lot of products because of a small problem, and do not cause or miss a product safety hazard due to a potentially huge problem, even if it is a small percentage.
Randomness of sampling
AQL sampling must ensure randomness of selected samples. In other words, AQL sampling criteria are only what you use as a reference for the number of samples. In order to ensure the rationality and comprehensiveness of the test results, it is necessary to ensure the comprehensiveness and randomness in the sampling process. As far as possible, sampling covers all production shifts in one lot, and is uniform and random based on quantity.
Will a PASS inspection based on the AQL sampling plan ensure that your products are actually in good condition?
Strictly speaking, this does not guarantee that the whole batch will be free of problems, but from a probability point of view, a product that has been approved by AQL standard testing and inspection is, in terms of risk, completely acceptable to you.
Also, we must also consider the professional and responsible attitude of the inspectors.
How Can inXpection Help You?
At inXpection, each of our employees has worked for many years at retailers known for superior quality products, has extensive product and quality experience, and is well trained to ensure the best quality for your products and protect your brand.
>> Contact us for a quotation now.
